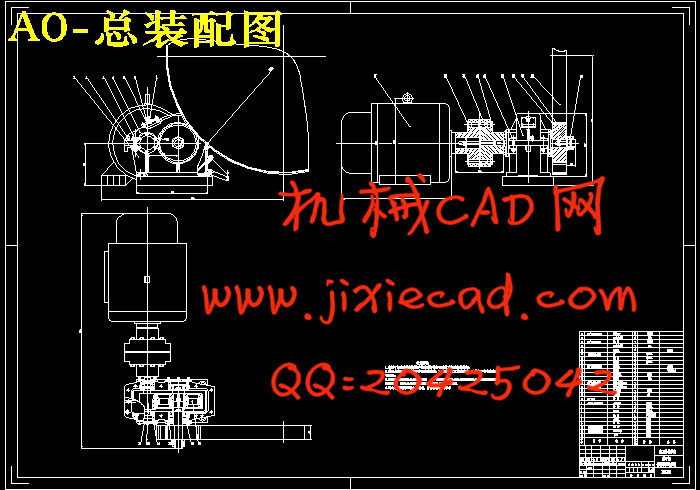
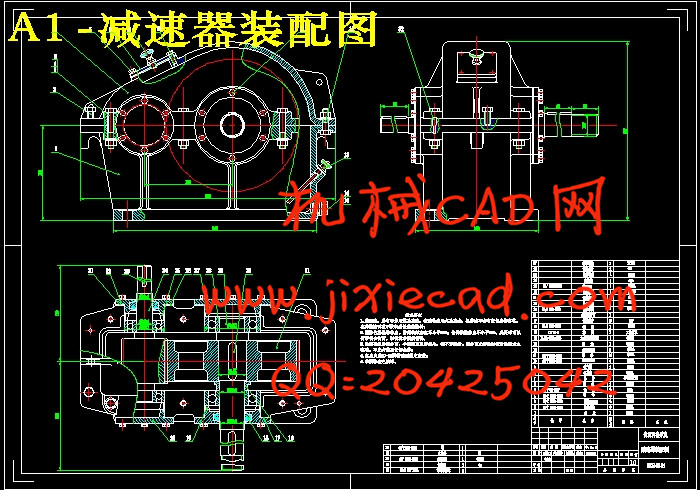
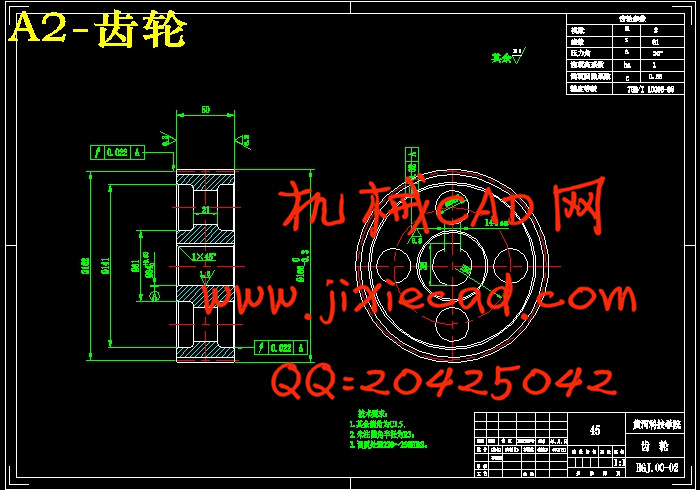
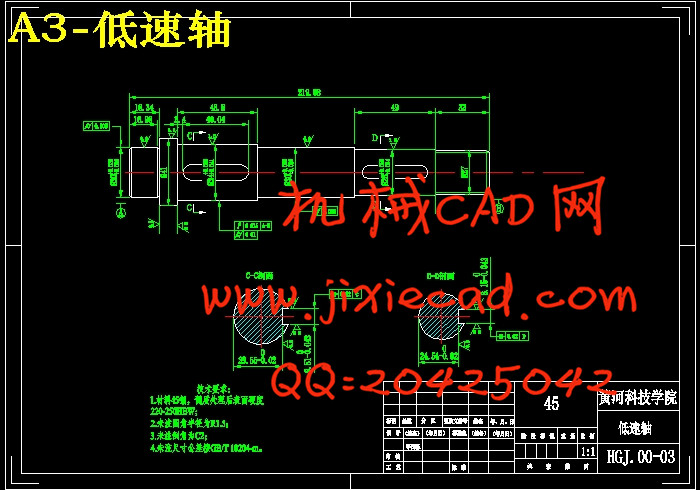
设计简介
Ø600×6000转筒烘干机传动系统设计
摘要
转筒烘干机也被称为滚筒干燥设备或圆筒烘干机,是一种处理大量物料的干燥器。转筒烘干机根据干燥介质与湿物料之间的传热方式分为直接传热转筒烘干机和间接传热转同烘干机。转筒烘干机由于运转可靠、操作弹性大、适应性强、处理量大,广泛使用于冶金、建材、轻工、化工、煤炭、医药矿产业中。
本文主要侧重于对转筒烘干机传动系统的设计。转筒烘干机的传动系统主要是通过联轴器将动力传入单级圆柱齿轮减速器,再通过圆柱齿轮传动,将动力传至筒式烘干机的滚筒,从而带动滚筒转动来烘干物料。
关键词:转筒烘干机,传动系统,设计
The drive syetem design of the Ø600×6000 drum dryer
abstract
Drum dryer was also called the drum drying equipment or cylinder dryer, it is a kind of handling a large material dryer. According to the dry and wet material medium between the way of heat transfer ,the drum dryer is divided into direct heat transfer drum dryer and indirect heat transfer drum dryer. Because of reliable operation, operating flexibility and adaptability, large quantity,drum dryer is widely used in metallurgy, building materials, light industry, chemical industry, coal, medicine in the mining industry .
This design is mainly focused on drive system design of the drum dryer in the paper . The drive system of the drum dryer is mainly through the coupling pass power into single-stage cylindrical gear reducer,then through the cylindrical gear transmission pass power into the roller of drum dryer,so as to drive the roller to dry material.
Key word:drum dryer, drive system,design
目录
1 绪论 1
1.1 烘干机的发展史 1
1.2 烘干机的研究状况 1
1.3 论文的研究内容 2
2 筒式烘干机传动方案 3
2. 1设计任务 3
2.2 传动方案的确定 3
3 传动装置总体设计 4
3.1 电动机的选择 4
3.1.1 电动机类型的类型和结构形式 4
3.1.2 电动机容量的选择 4
3.1.3 电动机转速的选择 5
3.2 传动系统总传动比的计算及分配 6
3.2.1 总传动比的计算 6
3.2.2 分配各级传动比 6
3.3 传动系统的运动和动力参数计算 6
3.3.1 各轴的转速 6
3.3.2 各轴的输入功率 6
3.3.3 各轴的输入转矩 7
3.4 减速器齿轮传动设计 7
3.4.1 选定齿轮类型、精度等级、材料及齿数 7
3.4.2 按齿面接触强度设计 8
3.4.3 按齿面弯曲强度计算 10
3.4.4 几何尺寸计算 11
3.5 开式齿轮传动设计 12
3.5.1 选定齿轮类型、精度等级、材料及齿数 12
3.5.2 按齿面接触强度设计 12
3.5.3 按齿面弯曲强度计算 15
3.5.4 几何尺寸计算 16
4 传动零件的设计 17
4.1 联轴器的选择 17
4.1.1 联轴器的分类 17
4.1.2 选择 17
4.2 轴系结构设计 18
4.2.1 高速轴的轴系结构设计 18
4.2.2 低速轴的轴系结构设计 19
4.3 轴承的选择 20
4.4 各轴键选择及其校核 21
4.4.1 高速级键的选择及校核 21
4.4.2 中间级键的选择及校核 22
4.4.3 低速级级键的选择及校核 22
5 减速器箱体及其附件 23
5.1 减速器箱体设计 23
5.2 减速器附件 24
5.2.1 视孔盖 24
5.2.2 放油螺塞 24
5.2.3 油标 24
5.2.3 通气孔 24
5.2.4 起吊装置 24
5.2.5 起盖螺钉 24
结 论 25
致 谢 26
参考文献 27
摘要
转筒烘干机也被称为滚筒干燥设备或圆筒烘干机,是一种处理大量物料的干燥器。转筒烘干机根据干燥介质与湿物料之间的传热方式分为直接传热转筒烘干机和间接传热转同烘干机。转筒烘干机由于运转可靠、操作弹性大、适应性强、处理量大,广泛使用于冶金、建材、轻工、化工、煤炭、医药矿产业中。
本文主要侧重于对转筒烘干机传动系统的设计。转筒烘干机的传动系统主要是通过联轴器将动力传入单级圆柱齿轮减速器,再通过圆柱齿轮传动,将动力传至筒式烘干机的滚筒,从而带动滚筒转动来烘干物料。
关键词:转筒烘干机,传动系统,设计
The drive syetem design of the Ø600×6000 drum dryer
abstract
Drum dryer was also called the drum drying equipment or cylinder dryer, it is a kind of handling a large material dryer. According to the dry and wet material medium between the way of heat transfer ,the drum dryer is divided into direct heat transfer drum dryer and indirect heat transfer drum dryer. Because of reliable operation, operating flexibility and adaptability, large quantity,drum dryer is widely used in metallurgy, building materials, light industry, chemical industry, coal, medicine in the mining industry .
This design is mainly focused on drive system design of the drum dryer in the paper . The drive system of the drum dryer is mainly through the coupling pass power into single-stage cylindrical gear reducer,then through the cylindrical gear transmission pass power into the roller of drum dryer,so as to drive the roller to dry material.
Key word:drum dryer, drive system,design
目录
1 绪论 1
1.1 烘干机的发展史 1
1.2 烘干机的研究状况 1
1.3 论文的研究内容 2
2 筒式烘干机传动方案 3
2. 1设计任务 3
2.2 传动方案的确定 3
3 传动装置总体设计 4
3.1 电动机的选择 4
3.1.1 电动机类型的类型和结构形式 4
3.1.2 电动机容量的选择 4
3.1.3 电动机转速的选择 5
3.2 传动系统总传动比的计算及分配 6
3.2.1 总传动比的计算 6
3.2.2 分配各级传动比 6
3.3 传动系统的运动和动力参数计算 6
3.3.1 各轴的转速 6
3.3.2 各轴的输入功率 6
3.3.3 各轴的输入转矩 7
3.4 减速器齿轮传动设计 7
3.4.1 选定齿轮类型、精度等级、材料及齿数 7
3.4.2 按齿面接触强度设计 8
3.4.3 按齿面弯曲强度计算 10
3.4.4 几何尺寸计算 11
3.5 开式齿轮传动设计 12
3.5.1 选定齿轮类型、精度等级、材料及齿数 12
3.5.2 按齿面接触强度设计 12
3.5.3 按齿面弯曲强度计算 15
3.5.4 几何尺寸计算 16
4 传动零件的设计 17
4.1 联轴器的选择 17
4.1.1 联轴器的分类 17
4.1.2 选择 17
4.2 轴系结构设计 18
4.2.1 高速轴的轴系结构设计 18
4.2.2 低速轴的轴系结构设计 19
4.3 轴承的选择 20
4.4 各轴键选择及其校核 21
4.4.1 高速级键的选择及校核 21
4.4.2 中间级键的选择及校核 22
4.4.3 低速级级键的选择及校核 22
5 减速器箱体及其附件 23
5.1 减速器箱体设计 23
5.2 减速器附件 24
5.2.1 视孔盖 24
5.2.2 放油螺塞 24
5.2.3 油标 24
5.2.3 通气孔 24
5.2.4 起吊装置 24
5.2.5 起盖螺钉 24
结 论 25
致 谢 26
参考文献 27