设计简介
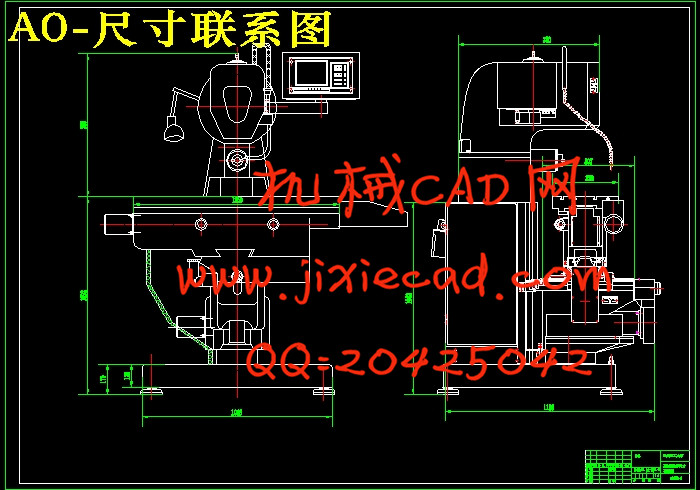
1、工作台尺寸(长×宽): 1100mm×300mm
2、工作台最大行程: 纵向 680mm 横向 270mm 垂直 380mm
3、快速移动速度: 10m/min
4、工作台定位精度 x、y、z ±0.03mm;
5、工作台重复定位精度 x、y、z ±0.02mm;
6、纵向、横向及垂直进给为微机控制,采用步进电机或直流伺服电机驱动,滚珠丝杠传动,脉冲当量0.010mm/脉冲。
7、实现功能:铣削平面、斜面、沟槽、齿轮等。
8、操作要求:起动、点动、单步运行、自动循环、暂停、停止
Reform process as follows: ( 1) the reformation of machine part, including the overall reconstruction scheme and vertical feed direction of reformation. Consisting mainly of ball screw pair and reaction stepper motor selection and calculation of vertical feeding mechanism assembly plan. ( 2) the electrical control design, including MCS-51 Series MCU and the expansion of the chip selection and electrical control diagram design.
Keywords: numerical control ,single-chip ,stepping motor , ball screw shaft ,reform
目 录
第1章 数控机床发展概述 1
1.1 我国数控机床发展现状及思考 1
1.1.1 不断加强技术创新是提高国产数控机床水平的关键 1
1.1.2 制造水平与管理手段依然落后 2
1.1.3 服务水平与能力欠缺也是影响国产数控机床占有率的一个重要因素 2
1.1.4 加大数控专业人才的培养力度 2
1.1.5 结语 3
1.2 数控机床及其特点 3
1.3 数控机床的经济分析 4
1.3.1 中小企业数控机床选用中存在的问题 4
1.3.2 数控机床选购的策略 4
1.4 数控机床的工艺范围及加工精度 6
1.5 数控机床的发展趋向 7
第2章 数控机床总体方案的制订及比较 11
2.1 机床数控化改造的意义 11
2.2 设计方案论证 12
3.1 科学选择数控刀具 14
3.1.1 选择数控刀具的原则 14
3.1.2 选择数控铣削用刀具 14
3.2 设置刀点和换刀点 15
3.3 确定切削用量 15
3.3.1 确定主轴转速 16
3.3.2 确定进给速度 16
3.3.3 确定背吃刀量 16
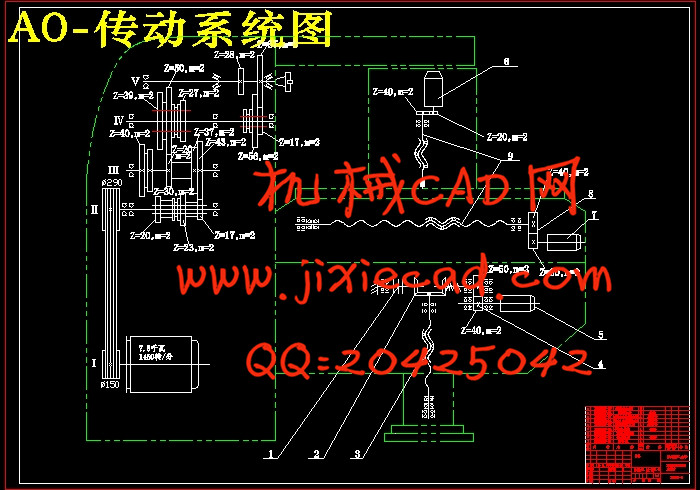
第4章 传动系统图的设计计算 17
4.1 对数控铣床主传动系统简介 17
4.2 对数控铣床主传动系统的要求 17
4.3 主传动的类型及方案选择 18
4.4 计算切削功率 19
4.4.1 切削力的计算 19
4.4.2 切削功率的计算 20
4.4.3 主轴转速范围的确定 20
4.5 计算主传动功率 20
4.6 分级变速箱的传动系统的设计及主轴电动机的功率的确定 21
4.6.1 变速级数Z的确定 21
4.6.2 电动机的功率的确定 22
4.6.3 电动机参数 22
4.6.4 分级变速箱的传动系统变速机构的确定 23
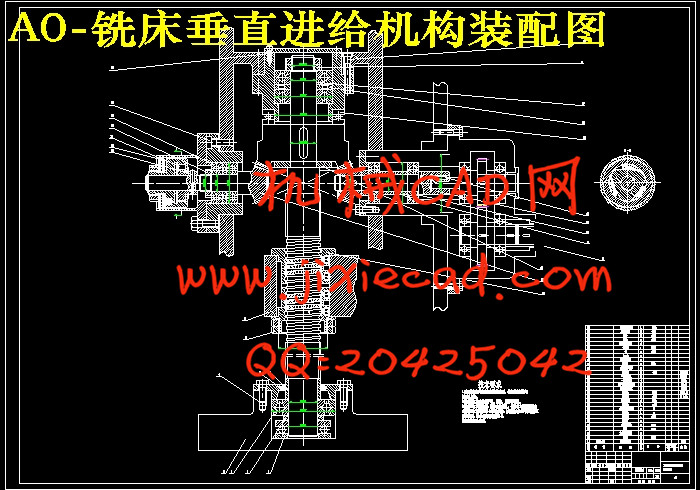
第5章 主要部件装配图的设计计算 24
5.1 确定系统脉冲当量 24
5.2 滚珠丝杠螺母副的设计,计算和选型 24
5.3 传动效率计算 27
5.4 垂直丝杠传动比计算 28
5.5 垂直丝杠步进电机的计算 28
第6章 机床硬件电路图的设计 31
6.1 微机控制系统组成及特点 31
6.1.1 微机控制系统的组成 31
6.1.2 微机数控系统的特点 31
6.2 微机控制系统设备介绍 32
6.2.1 主控制器CPU的选择 32
6.2.2 存储器电路的扩展 33
6.2.3 I/O口电路的扩展 34
6.2.4 步进电机驱动电路 35
6.2.5 其它辅助电路设计 36
6.3 程序部分 36
总结与展望 41
参考文献 42
致 谢 43
2、工作台最大行程: 纵向 680mm 横向 270mm 垂直 380mm
3、快速移动速度: 10m/min
4、工作台定位精度 x、y、z ±0.03mm;
5、工作台重复定位精度 x、y、z ±0.02mm;
6、纵向、横向及垂直进给为微机控制,采用步进电机或直流伺服电机驱动,滚珠丝杠传动,脉冲当量0.010mm/脉冲。
7、实现功能:铣削平面、斜面、沟槽、齿轮等。
8、操作要求:起动、点动、单步运行、自动循环、暂停、停止
摘 要
针对现有常规X6132万能升降台铣床的缺点提出数控改造方案和单片机系统设计,提高加工精度和扩大机床使用范围,并提高生产率。本论文说明了万能升降台铣床的数控化改造的设计过程,较详尽地介绍了X6132万能升降台铣床机械改造部分的设计及数控系统部分的设计。采用以8031为CPU的控制系统对信号进行处理,由I/O接口输出步进脉冲,经一级齿轮传动减速后,带动滚动丝杠转动,从而实现垂直的进给运动。
改造过程如下:(1)机械部分的改造,包括总体改造方案的确定和进给方向的改造。主要包括对滚珠丝杠螺母副及反应式步进电机的计算选择及垂直进给机构装配图方案的制定。(2)电气控制部分的设计,主要包括MCS-51系列单片机及扩展芯片的选用和电气控制图的设计。
关键词:数控,单片机,步进电机,滚珠丝杠,改造
ABSTRACT
Conventional existing X6132 universal lifting platform milling machine numerical control transformation of the disadvantages of the proposed scheme and design of a single chip microcomputer system, improve the processing precision and extend the machine's usage, and to improve productivity. This paper illustrates the universal lifting platform milling machine numerical control transformation of the design process, a more detailed description of the X6132 universal lifting platform milling machine transformation part of the design and numerical control system design. Using 8031 as the CPU control system of signal processing by the I/O interface, and output the step pulse, through a gear reducer, drive the leading screw to roll, so as to realize the vertical movement of the feed.针对现有常规X6132万能升降台铣床的缺点提出数控改造方案和单片机系统设计,提高加工精度和扩大机床使用范围,并提高生产率。本论文说明了万能升降台铣床的数控化改造的设计过程,较详尽地介绍了X6132万能升降台铣床机械改造部分的设计及数控系统部分的设计。采用以8031为CPU的控制系统对信号进行处理,由I/O接口输出步进脉冲,经一级齿轮传动减速后,带动滚动丝杠转动,从而实现垂直的进给运动。
改造过程如下:(1)机械部分的改造,包括总体改造方案的确定和进给方向的改造。主要包括对滚珠丝杠螺母副及反应式步进电机的计算选择及垂直进给机构装配图方案的制定。(2)电气控制部分的设计,主要包括MCS-51系列单片机及扩展芯片的选用和电气控制图的设计。
关键词:数控,单片机,步进电机,滚珠丝杠,改造
ABSTRACT
Reform process as follows: ( 1) the reformation of machine part, including the overall reconstruction scheme and vertical feed direction of reformation. Consisting mainly of ball screw pair and reaction stepper motor selection and calculation of vertical feeding mechanism assembly plan. ( 2) the electrical control design, including MCS-51 Series MCU and the expansion of the chip selection and electrical control diagram design.
Keywords: numerical control ,single-chip ,stepping motor , ball screw shaft ,reform
目 录
第1章 数控机床发展概述 1
1.1 我国数控机床发展现状及思考 1
1.1.1 不断加强技术创新是提高国产数控机床水平的关键 1
1.1.2 制造水平与管理手段依然落后 2
1.1.3 服务水平与能力欠缺也是影响国产数控机床占有率的一个重要因素 2
1.1.4 加大数控专业人才的培养力度 2
1.1.5 结语 3
1.2 数控机床及其特点 3
1.3 数控机床的经济分析 4
1.3.1 中小企业数控机床选用中存在的问题 4
1.3.2 数控机床选购的策略 4
1.4 数控机床的工艺范围及加工精度 6
1.5 数控机床的发展趋向 7
第2章 数控机床总体方案的制订及比较 11
2.1 机床数控化改造的意义 11
2.2 设计方案论证 12
3.1 科学选择数控刀具 14
3.1.1 选择数控刀具的原则 14
3.1.2 选择数控铣削用刀具 14
3.2 设置刀点和换刀点 15
3.3 确定切削用量 15
3.3.1 确定主轴转速 16
3.3.2 确定进给速度 16
3.3.3 确定背吃刀量 16
第4章 传动系统图的设计计算 17
4.1 对数控铣床主传动系统简介 17
4.2 对数控铣床主传动系统的要求 17
4.3 主传动的类型及方案选择 18
4.4 计算切削功率 19
4.4.1 切削力的计算 19
4.4.2 切削功率的计算 20
4.4.3 主轴转速范围的确定 20
4.5 计算主传动功率 20
4.6 分级变速箱的传动系统的设计及主轴电动机的功率的确定 21
4.6.1 变速级数Z的确定 21
4.6.2 电动机的功率的确定 22
4.6.3 电动机参数 22
4.6.4 分级变速箱的传动系统变速机构的确定 23
第5章 主要部件装配图的设计计算 24
5.1 确定系统脉冲当量 24
5.2 滚珠丝杠螺母副的设计,计算和选型 24
5.3 传动效率计算 27
5.4 垂直丝杠传动比计算 28
5.5 垂直丝杠步进电机的计算 28
第6章 机床硬件电路图的设计 31
6.1 微机控制系统组成及特点 31
6.1.1 微机控制系统的组成 31
6.1.2 微机数控系统的特点 31
6.2 微机控制系统设备介绍 32
6.2.1 主控制器CPU的选择 32
6.2.2 存储器电路的扩展 33
6.2.3 I/O口电路的扩展 34
6.2.4 步进电机驱动电路 35
6.2.5 其它辅助电路设计 36
6.3 程序部分 36
总结与展望 41
参考文献 42
致 谢 43