设计简介
摘要
齿轮是机器和仪器中重要的机械零件之一,常用它传递运动和动力。由于齿轮用途甚广,要求各异,形状复杂,几何参数多,在制造和安装中会产生一定的误差,因而会影响其使用质量。为了满足齿轮的使用要求,必须对它进行检测。齿轮径向综合误差对齿轮的传动精度有很大的影响,也是用于综合检测齿轮的重要指标。目前,对于径向跳动的检测主要采用手动及人工误差处理的机械式的测量方法,这种传统的检测方法既耗时又难以保证检测结果的准确性。为了提高齿轮径向跳动的检测精度和效率,必须对传统测量仪器进行智能化改进。本设计针对传统的齿轮双面啮合检测仪检测效率低、误差率较高等缺点,采用电子技术对其进行改进,实现了检测的自动化、数字化,提高了检测的效率、精度和可靠性。改进后的齿轮双面啮合检测仪主要由机械本体部分、电涡流传感器、步进电机及控制电路组成,具有体积小、重量轻、操作方便、稳定性好等特点。
关键词 双面啮合检测仪 齿轮径向综合误差 步进电机 电涡流传感器
Abstract
Gear is one of the important components in the machine and instrument, which is often used transmit movement and power. As Gear is used very wide and has varied requirements, complex shape and geometric parameters, most of the manufacture and installation will have a certain degree of error, thus will affect the using quality. In order to meet the requirement of gear, it must be tested. The total composite radial error of gear has a great influence on gear transmission accuracy. It is an important index of gear for synthesis measurement. At present, the traditional gear run-out error measuring system is time-cost and hard to acquire higher precision. So it is meaningful and necessary to improve the traditional radial run-out measuring system.Against disadvantages of the traditional gear double flank rolling tester instrument such as lower efficiency, higher error and etc, the traditional gear two flank testing instrument is improved by using the electric technology. The automation, numeralization for gear testing are realized and the testing efficiency, precision and reliability are increased. The improved double flank rolling tester is mainly made up of mechanical body parts, eddy current sensor, stepper motors and control circuits, and has the characteristics of small size, light weight, easy to operate, good stability and so on.
Key words : double flank rolling tester the total composite radial error of gear stepper motors eddy current sensor
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 课题任务 1
1.2 齿轮检测技术的发展 1
1.3 课题主要工作内容 3
1.4 本章小结 3
第2章 机械结构部分的改造设计 4
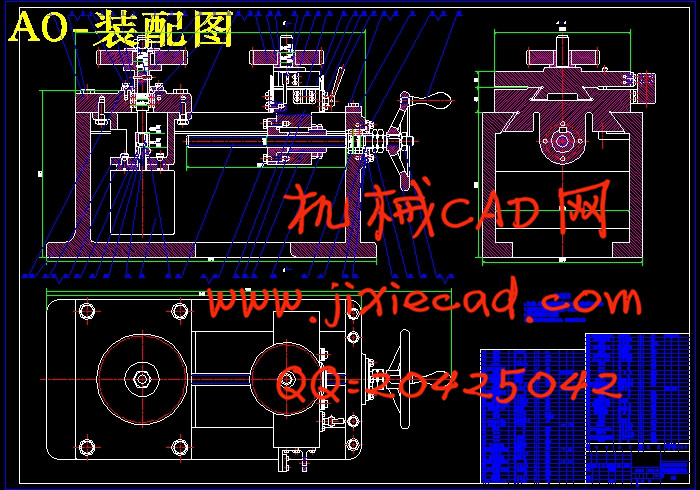
2.1 齿轮双啮仪的工作原理 4
2.2 轴的设计 5
2.2.1 轴的计流程 5
2.2.2 轴的材料和毛坯 6
2.2.3 零件在轴上的定位形式 6
2.2.4 轴的设计计算 7
2.3 丝杠螺母副的设计计算 9
2.3.1 滚珠丝杠副的组成 9
2.3.2 耐磨性计算 10
2.3.3 丝杠的强度计算 12
2.3.4 螺母凸缘的强度计算 14
2.3.5 丝杠的稳定性计算 14
2.4 滚动轴承的选用和计算 15
2.4.1 滚动轴承类型的选择 15
2.4.2 滚动轴承的构造及材料选择 16
2.4.3 滚动轴承的校核计算 17
2.5 联轴器的选用和计算 18
2.5.1 联轴器的类型 18
2.5.2 联轴器的选择原则 18
2.5.3 联轴器的选取计算 19
2.6 螺纹联接的选用计算 21
2.6.1 螺纹联接 21
2.6.2 螺纹联接的强度计算 21
2.7 键的选用 24
2.7.1 键联接的分类 24
2.7.2 键联接的强度计算 25
2.8 销的选用 26
2.8.1 销的分类 26
2.8.2 销的强度计算 26
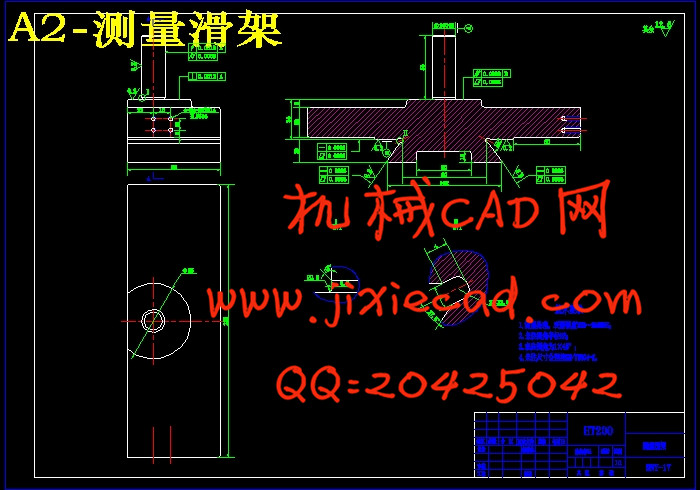
2.9 导轨的设计 27
2.9.1 导轨的作用和设计要求 27
2.9.2 本设计导轨的主要结构 27
第3章 动力驱动部分的设计 29
3.1 步进电机的定义 29
3.2 步进电机的分类 29
3.3 步进电机的工作原理 29
3.4 步进电机的性能指标 31
3.4.1 步进电机的静态性能指标 31
3.4.2 步进电机的动态性能指标 31
3.4 步进电机的选择 33
3.4.1 种类的选择 33
3.4.2 型号的选择 33
3.5 本章小结 34
第4章 传感测试及控制电路部分设计 35
4.1 电涡流传感器的基本原理 35
4.2 电涡流传感器的选择 36
4.3 控制电路部分的原理框图 37
4.4 单片机的选择 38
4.4.1 8051的引脚功能 38
4.4.2 复位电路 39
4.4.3 时钟电路 40
4.5 A/D转换器的选择 40
4.6译码器的选择 41
4.7键盘 43
4.7.1矩阵式键盘的结构和原理 43
4.7.2矩阵式键盘的识别 44
4.8总体电路图 45
4.9本章小结 45
结 论 46
致 谢 47
参考文献 48