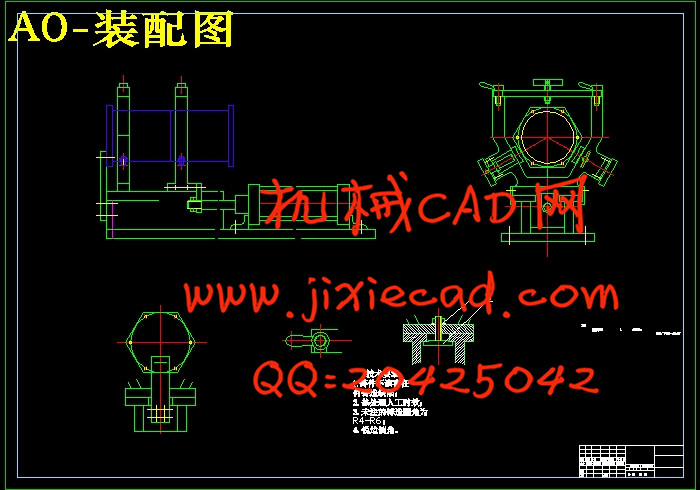
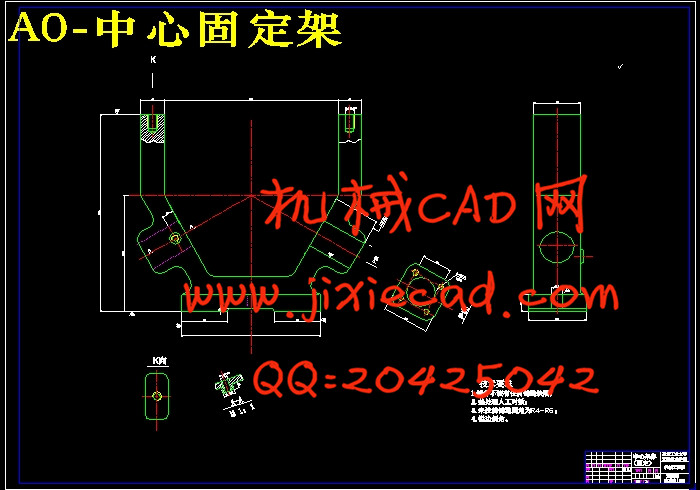
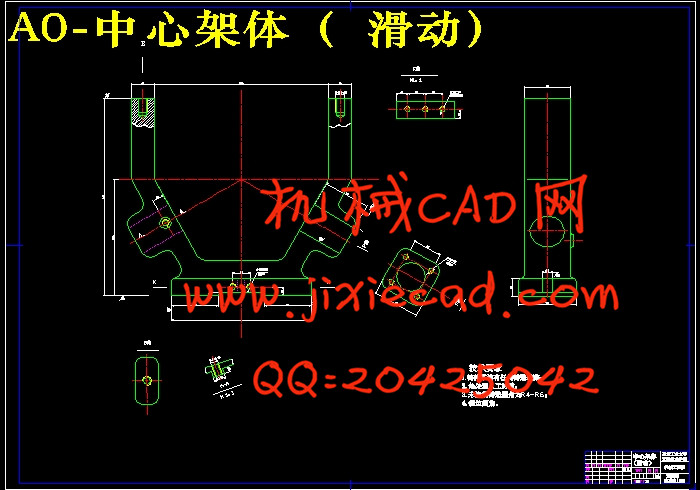
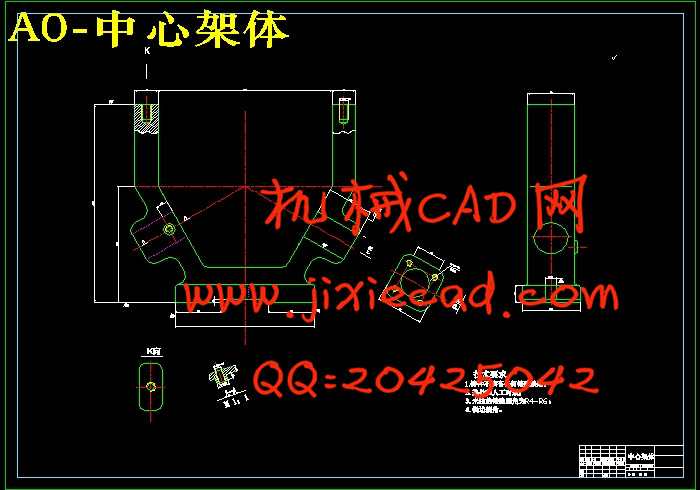
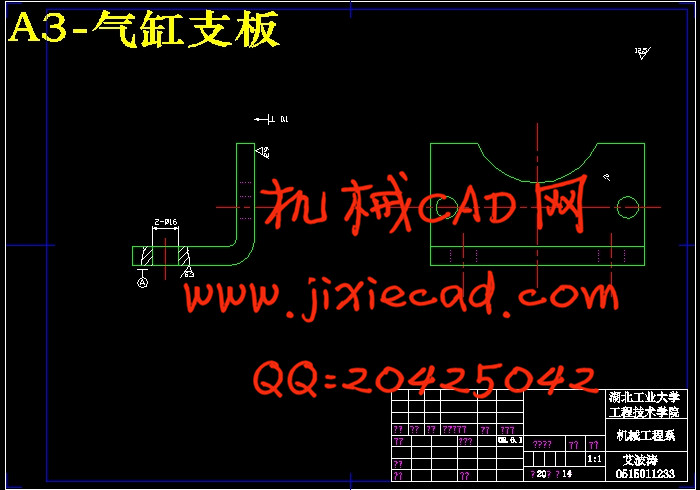
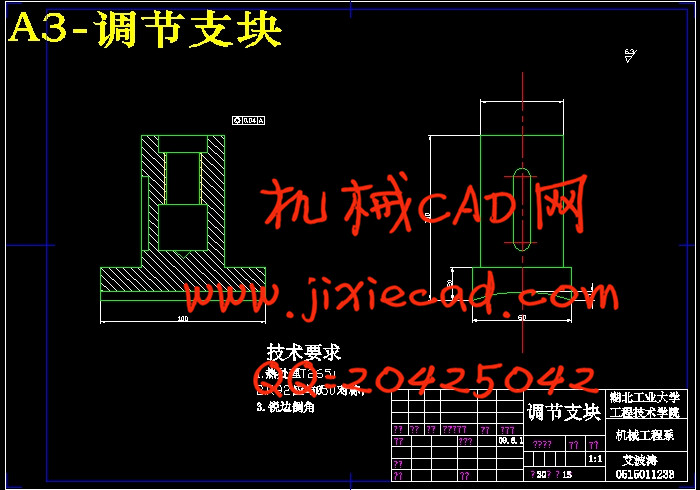
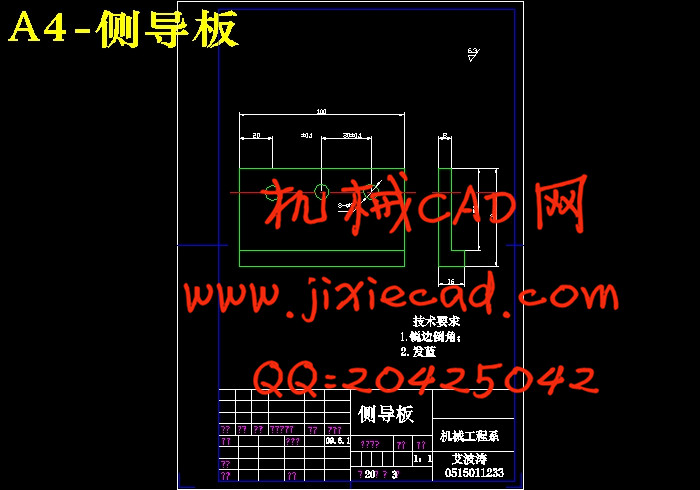
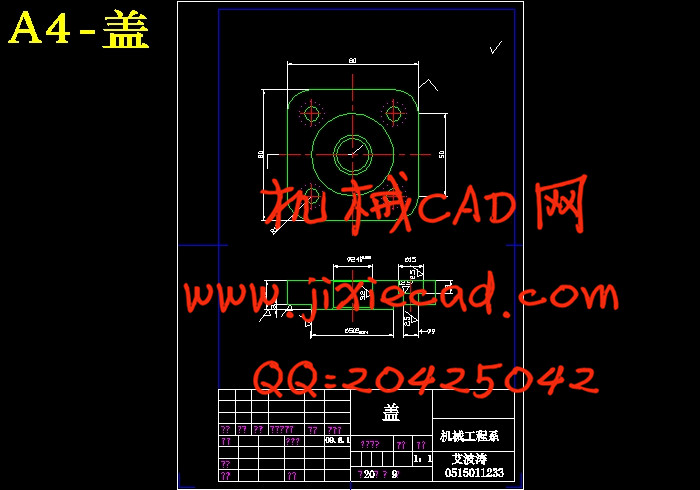
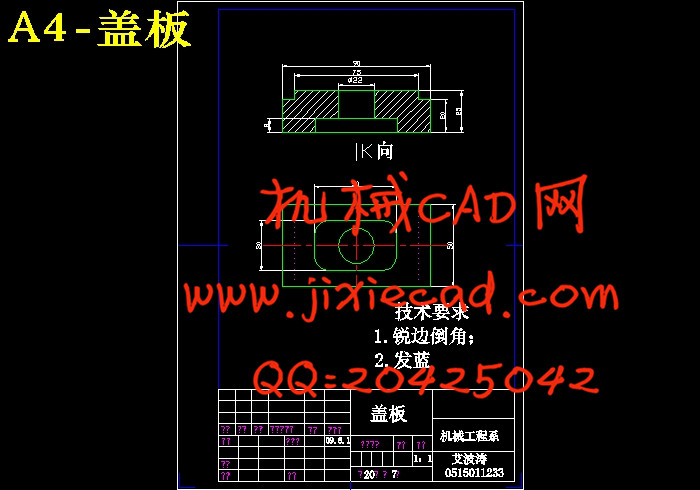
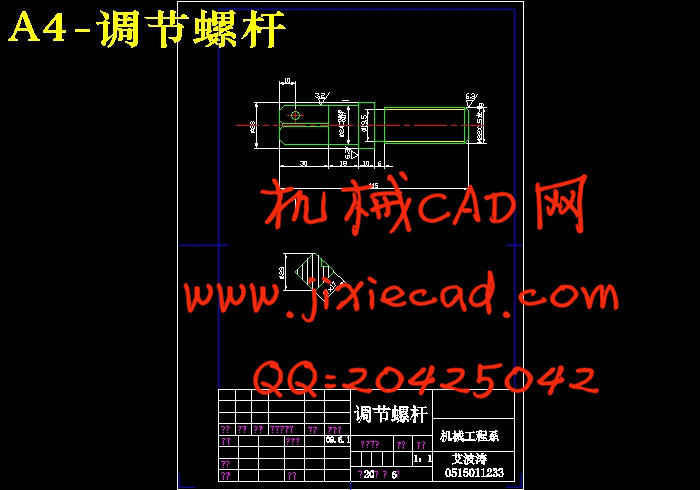
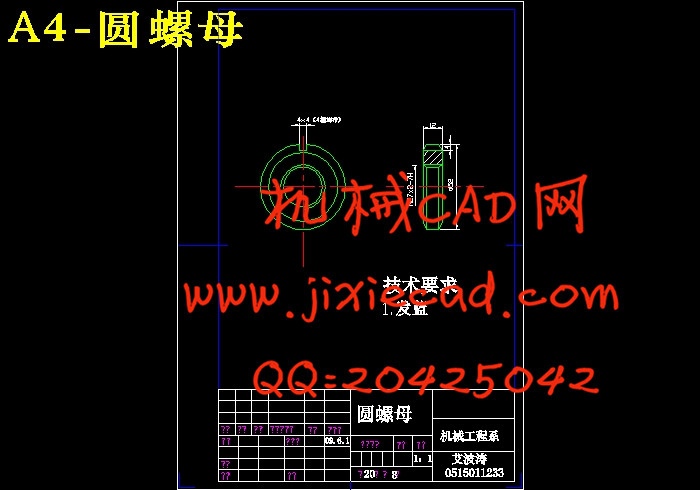
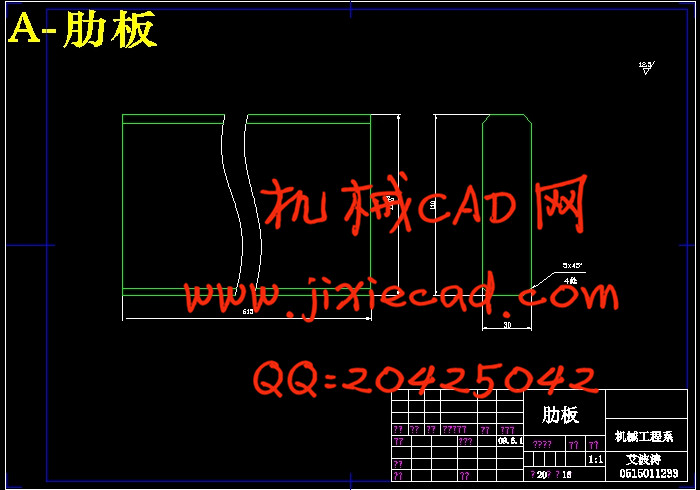
设计简介
摘 要
电力机车本身不带原动机,靠接受接触电网送来的电流作为能源,由牵引电动机驱动机车的车轮。电力机车具有功率大、热效率高、速度快、过载能力强和运行可靠等主要优点,而且不污染环境,特别适用于运输繁忙的铁路干线和隧道多,坡度大的山区铁路。电力机车的工作原理,接触导线上的电流,经受电弓进入机车后经过主断路器再进入主变压器,交流电从主变压器的牵引绕组经过硅机组整流后,向六台分两组并联的牵引电动机集中供应直流电,使牵引电动机产生转矩,将电能转变为机械能,经过齿轮的传递驱动机车动轮转动。
受电弓动作原理:
(1)升弓:压缩空气经电空阀均匀进入传动气缸,气缸活塞压缩气缸内的降弓弹簧,此时升弓弹簧使下臂杆转动,抬起上框架和滑板,受电弓匀速上升,在接近接触线时有一缓慢停滞,然后讯速接触接触线。
(2)降弓:传动气缸内压缩空气经受电弓缓冲阀迅速排向大气,在降弓弹簧作用下,克服升弓弹簧的作用力,使受电弓迅速下降,脱离接触网。
关键词:电力机车 受电弓 气缸 活塞
Abstract
Non-electric locomotive prime mover itself, by the acceptance of the Catenary current as a source of energy delivered by the traction motor drive the wheels of locomotives. Electric locomotive with power, and thermal efficiency, high speed, overloading strong and reliable operation of the major advantages and do not pollute the environment, especially suitable for heavy transport and tunnel rail link and more, steep slope and the mountain railway.The working principle of electric locomotive, the current contact wire, stood the locomotive pantograph After entering the main circuit breaker re-entering the main transformer, alternating current from the main traction transformer winding through silicon rectifier unit, the two groups of six parallel to the traction motor focus on the supply of direct current to produce torque traction motor, electrical energy into mechanical energy, through the transmission gear-driven locomotive drive wheels turning.
Pantograph action principle:
(1) bow up: electro-pneumatic valve by compressed air evenly into the drive cylinder, the cylinder piston within the cylinder compression spring bow down, bow or spring at this time so that the next boom rotation, raised his skateboard on the framework and by pantograph uniform increase near the contact line when there is a slow stagnation, and then contact the contact line rapidly.
(2) bow down: Transmission of compressed air cylinder valve to withstand the rapid pantograph buffer row into the atmosphere, in the spring bow down under the arch or to overcome the spring force, so that the pantograph to drop rapidly from the catenary.
Key words: ectric locomotive pantograph cylinder piston
目 录
摘 要 iAbstract ii
1 绪论 1
1.1电力机车 1
1.2受电弓 3
2 受电弓风缸主体部分的设计 7
2.1 夹具的组成 7
2.2 夹具的类型 7
2.3 工件结构特点分析 8
2.4 工件定位方案和定位元件的设计 8
2.5 夹紧方案和夹紧元件的设计 8
2.6 夹具体的设计 8
2.7 误差的分析与计算 9
2.8 夹具精度分析计算 10
3 液压系统的设计 13
3.1方案设计 13
4 液压系统元件的选择 16
4.1 液压系统的设计计算 16
4.2 液压系统中各元件的选择 16
4.2.1 泵与马达的选择 16
4.2.2 联轴器的选择 19
4.2.3 液压介质的选择 19
4.2.4 换向阀的选择 20
4.2.5 溢流阀的选择 22
4.2.6 单向阀的选择 22
4.2.7 液控单向阀的选择 23
4.2.8 冷却器的选择 23
结论 25
致谢 26
参考文献 27